
However, it is not without its drawbacks. Natural gas is also easy to transport through pressurized pipelines.Īll of this would appear to make natural gas the perfect fuel. It does produce carbon dioxide, which is a greenhouse gas, but all organic compounds also generate carbon dioxide on combustion. It is also an excellent fuel, burning with a high heat output and little in the way of unwanted pollution. It is hydrogenrich, since methane has a carbon to hydrogen ratio of 1:4. Natural gas is mostly methane with small quantities of ethane and other gases mixed in. This is a generic term for the light hydrocarbon fractions found associated with most oil deposits. The third major fossil fuel is natural gas. A great deal of research has been done on the liquefaction of coal but with little economically viable success. The other significant disadvantage of coal is that it is not liquid, making it awkward to transport and store and limiting its use in applications like automobiles. Indeed, it is the coal burning power plants of the eastern United States that are responsible for much of the acid rain and environmental damage observed in upstate New York and eastern Canada. It is a very dirty fuel that produces a large amount of unburned hydrocarbon, particulate, and -most damaging of all -significant quantities of sulfur dioxide byproducts. Unfortunately, as a fuel source, coal has many disadvantages. The proven reserves of minable coal are sufficient to supply the industrial needs of modern society for the next four to five hundred years. Minable coal is defined as 50% of the coal in a seam of at least 12 in thickness. The carbon to hydrogen ratio in coal is close to 1:1 (depending upon the type of coal), whereas the carbon to hydrogen ration in petroleum is closer to the 1:2 value expected for a hydrocarbon chain. Consequently, coal is more of a polymeric substance than petroleum and is found as a solid not a liquid. The resulting material still has some of the original lignin-like structure exhibiting many fused rings and a large fraction of aromatic compounds.

Coal also originates from decayed vegetative material buried eons ago, but the process is slightly different, being less oxidizing. The second most prominent and naturally most abundant fossil fuel is coal. Indeed, many food compounds and pharmaceuticals owe their synthesis to a petrochemical precursor. Smaller fractions are turned into fuel oil (27%), jet fuel (7.4%), and other miscellaneous fuels, while the small fraction (about 10%) is used for the synthesis of the thousands of petrochemicals used in our daily lives. Over 40% all of all production ends up consumed in automobiles and such. The principal use of petroleum is the production of gasoline. Fully half of the energy consumed in the United States is from petroleum used to produce fuels for automobiles, recreational vehicles, home heating, or industrial production. This is a mixture of light, simple hydrocarbons dominated by the fractions with 6 to 12 carbons but also containing some light hydrocarbons (e.g., methane and ethane).

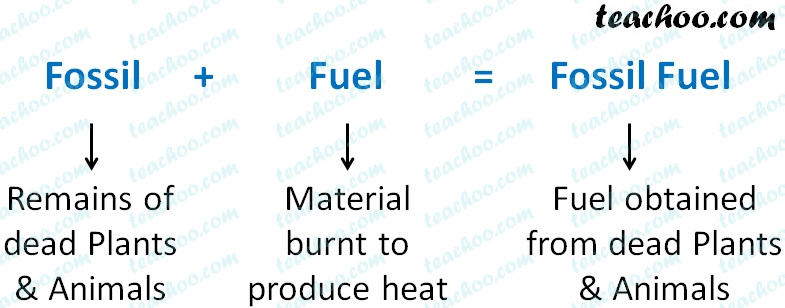
They are so named because they originate from the decayed and fossilized remains of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago.įossil fuels can be separated into three categories. Chemical fuels or the fossil fuels are useful reserve of fuels and are therefore used extensively to satisfy the demands of an energy-dependent civilization.įossil fuels are principally hydrocarbons with minor impurities. Wood, gasoline, coal, and any number of other fuels have energy-rich chemical bonds created using the energy from the Sun, which is released when the fuel is burned (i.e., the release of chemical energy). The most common form of oxidation is the direct reaction of a fuel with oxygen through combustion. This energy is captured in chemical bonds through processes such as photosynthesis and respiration. A fuel is any compound that has stored energy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
